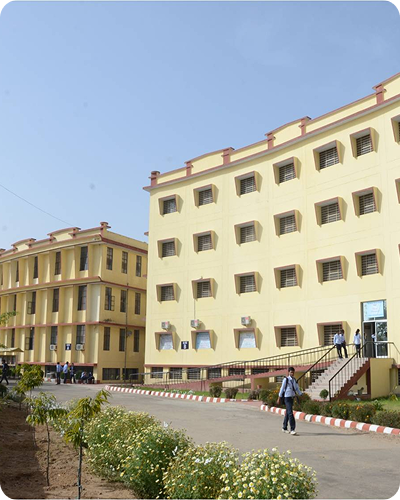
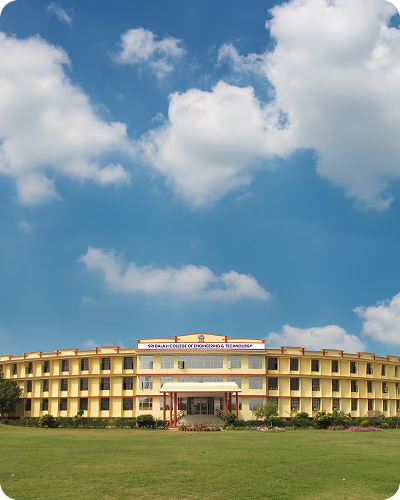
Welcome to Sri Balaji College of Engineering & Technology, Jaipur
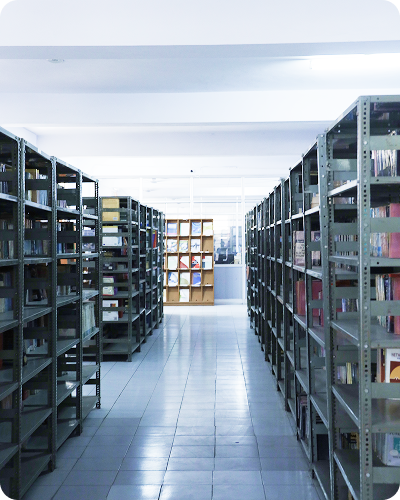
College Life
Access to world-class learning and inspirational environment to study with advanced facilities to provide best learning.
Skilled Lecturers
Our dedicated and highly qualified teaching staff is committed to ensure that every learner develops to his/her full potential.
Why Sri Balaji
At Balaji, we believe in nurturing leaders who excel not just in their careers, but also in character, compassion, and cultural values.
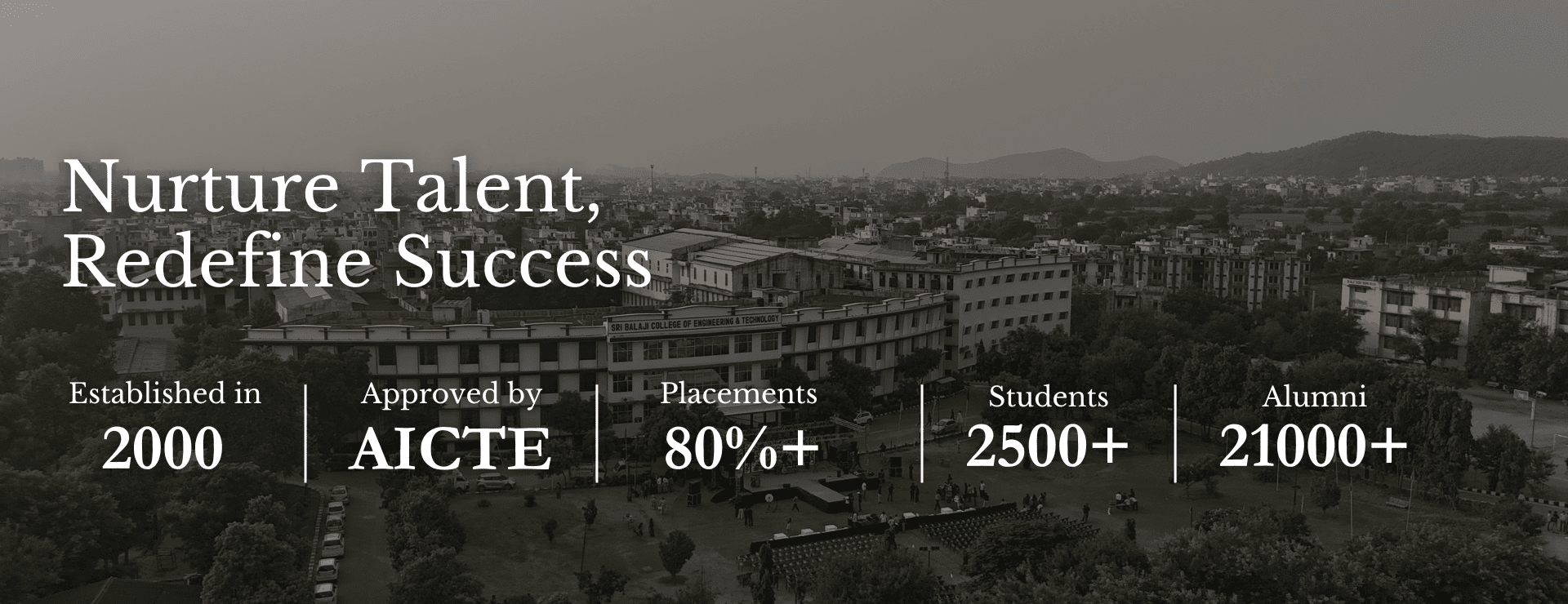
About Sri Balaji College of Engineering & Technology
Sri Balaji College of Engineering & Technology has been established in the year 2000 with due approval by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), New Delhi and affiliation to Rajasthan University, Jaipur.
Offering B.Tech, M.Tech, Ph.D., and MCA programs, it stands as a hub of innovation and excellence in engineering education.
Honoring the legacy of Late Prof. Alam Singh, the college continues to inspire future technocrats.
3000+
Campus Placement
2K+
Global Student
25
Years Of Academic Legacy
Brief Overview of Sri Balaji College of Engineering and Technology, Jaipur
Sri Balaji College of Engineering and Technology (SBCET), founded in 2000, is a well-known college in Jaipur, Rajasthan, that belongs to the Sri Balaji Group. The college operates under Rajasthan Technical University and is AICTE-approved to deliver complete studies and practical learning to help students gain strong professional skills. It prepares students for the real world by bridging the gap between academia and industry. Providing hands-on learning accompanied by excellent research methods combined with teaching techniques and training standards.
Key Highlights:
Modern Facilities: World-class facilities which provide students the chance to develop themselves through both academic and personal level.
Great Job Opportunities: The college has a Training and Placement Office that helps students prepare for job placement and ensures they secure strong hiring outcomes.
Variety of Courses: The college offers programs in Civil, Electrical, Mechanical, Electronics & Communication, and Computer Science Engineering, along with MCA studies.
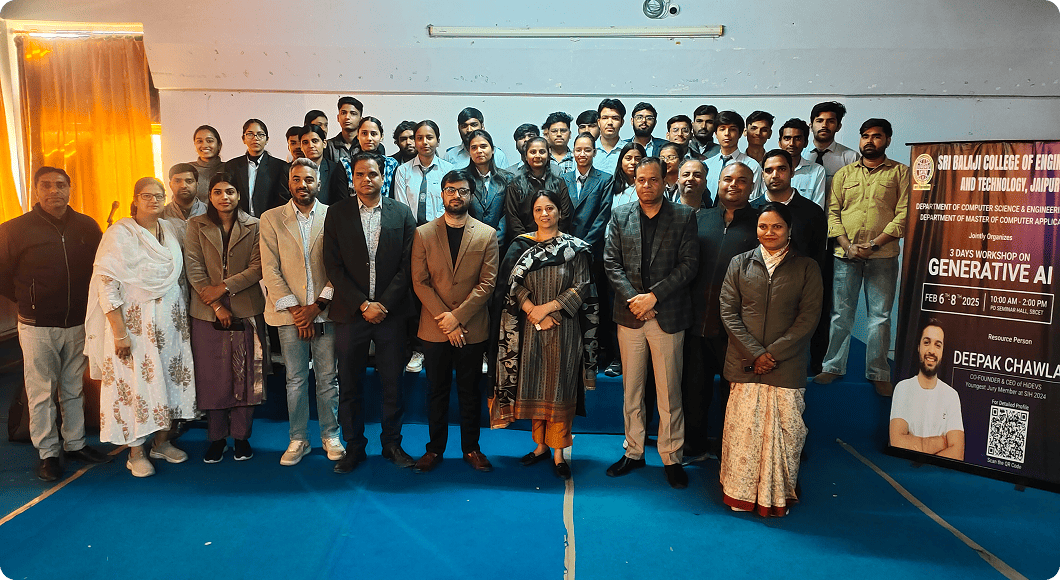
Overall Student Growth: The college organises seminars, workshops, guest lectures, and aptitude programs to help students in various areas.
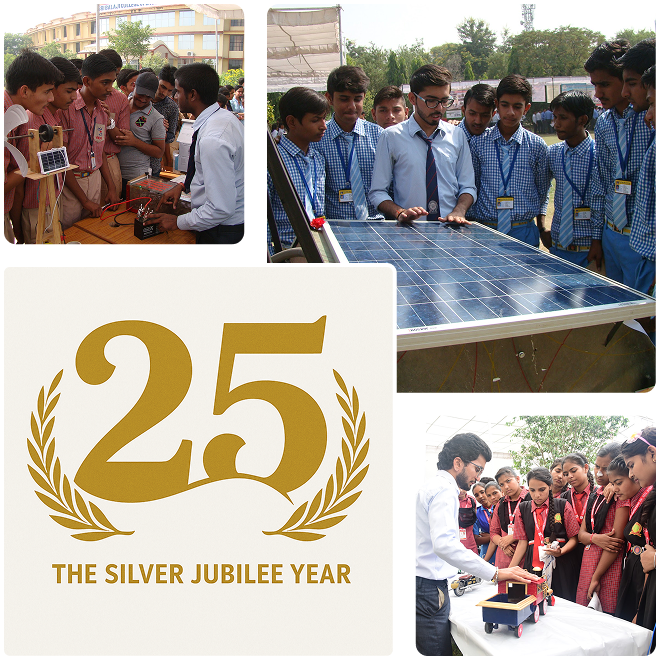

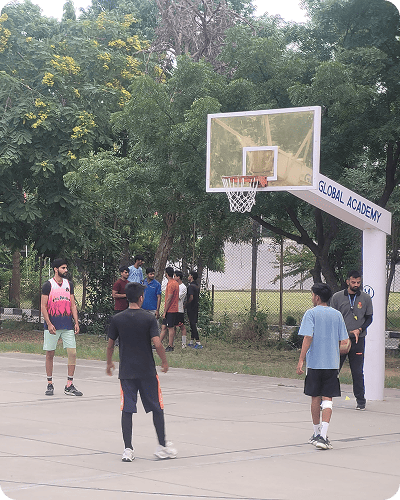
Campus Life @ Sri Balaji College of Engineering and Technology
Placement Partners
















































Our Blogs
Scan to Pay and Complete
Your Transaction!
No more long queues, just scan and complete your college fee payment in seconds - Fast, secure, and hassle-free.

Hear Them Speak

Admissions Now Open at Sri Balaji College - Apply Now for a Bright Future!
Sri Balaji College admissions are open. For academic fans and those seeking industry exposure, this is a once in a lifetime chance to enroll in one of the leading educational colleges. Sri Balaji College has a progressive faculty with good infrastructure and placement support which means it takes holistic care of the students.
Do not miss out in giving the college where you get talent, and also your great future companion for a good career.
Apply NowImportant Announcements
-
Deposition of Affiliation/Inspection & variation in intake fee for Academic Session 2025-26
-
Advt. for the one post of JRF (on purely Temporary Basis) under ISRO-RACS Project in the Metallurgical and Materials Engg. Dept.
-
Office order regarding Insurance policy of RTU authority and employees
-
Advt. for the one post of JRF (on purely Temporary Basis) under ISRO-RACS Project in the Metallurgical and Materials Engg. Dept.
-
Advt. for the one post of JRF (on purely Temporary Basis) under ISRO-RACS Project in the Metallurgical and Materials Engg. Dept.
-
Office order regarding Insurance policy of RTU authority and employees
Recent Activities


Upcoming Events
14
Feb
Literature Festival jaipur
14
Feb
Literature Festival jaipur
14
Feb
Literature Festival jaipur
14
Feb
Literature Festival jaipur
14
Feb
Literature Festival jaipur